Determine the Internal Energy Change of Hydrogen
The Shomate Equation for the ideal gas heat capacity is. C the cv value at room temperature.

Energy Diagrams For The Transfer Of Internal Energy Between A System And Its Surroundings The Change I Chemistry Education Chemistry Classroom Internal Energy
Determine the internal energy change of hydrogen in kJkg as it is heated.

. The internal energy change of hydrogen gas during a heating process is to be determined using an empirical specific heat relation constant specific heat at average temperature and constant specific heat at room temperature. The system had 20 cal endothermic reaction and 02 cal expansion. Plug in values for the temperatures and the constants to get.
The enthalpy change associated with a temperature change for an ideal gas can be determined from. The internal energy change of hydrogen gas during a heating processes to be determined using an empirical specific heat relation the constant specific heat average temperature and the constant specific heat at room temperature. Determine the internal energy change of hydrogen in kJkg as it is heated from 200 to 900 K using.
Combining Eqns 1 2 and 3 and integrating yields. 1 4-63 Determine the internal energy change of hydrogen in kJkg as it is heated from 200 to 800 K using a the empirical specific heat equation as a function of temperature Table A 2c b the cv value at the average temperature Table A-2b and c the cv value at room temperature Table A 2a. Determine the internal energy change Δu of hydrogen in kJkg as it is heated from 200 to 800 K using a the empirical specific heat equation as a function of temperature Table A2c b the cv value at the average temperature Table A2b and c the cv value at room temperature.
Determine the internal energy change Du of hydrogen in kJkg as it is heated from from CHEMICAL E 220 at MARA University of Technology. From 200 to 800 K using a the empirical specific heat equation as a function of. Temperature Table A 2c b the cv value at the average temperature Table A-2b and.
Determine the change in internal energy of as follows. As a function of temperature. Comment on your answers.
Determine the internal energy change u of hydrogen in kJkg as it is heated from 200 to 800 K using a The empirical specific heat equation as a function of temperature Table A2c b The CV value at the average temperature Table A2b. We need to convert mol to kg. 1 L 1E-3 m3.
Once boiled this volume of water changes to 1671 Liters of steam at 100 degrees C Assume the pressure remains constantat 1 atm. From ideal gas specific heat of various gases. Determine the internal energy change displaystyletriangleu of hydrogen in kJkg as it is heated from 200 to 800 K using a the empirical specific heat equation as a function of temperature Table A-2c b the displaystylec_v value at the average temperature Table A-2b and c the displaystylec_v value at room temperature Table A-2a.
The internal energy change could be defined as the following. R is a constant8314J molK U32 831420024942 Jmol. The system released 15 cal heat and the volume became half with 0.
NmM for hydrogen M2. The internal energy change of hydrogen gas during a heating processes to be determined using an empirical specific heat relation the constant specific heat average temperature and the constant specific heat at room temperature. Determine the change in internal energy of 1 kg of water at 100 degrees C when it is fully boiled.
The empirical specific heat equation as function of temperature Table A-2c The c_v value at the average temperature Table A-2b The c_v value at room temperature. Hendikeps2 and 2 more. Now we will use the empirical relation for part A which says for which is for CP as a function of T and we get this from our.
Δ u c v T 2 T 1 Delta uc_v T_2-T_1 Δ u c v T 2 T 1 Δ u 10183 800 200 6110 K J K g Delta u10183times 800-2006110 mathrm KJKg Δ u 10183 800 200 6110 KJKg. A Using the empirical relation for. Determine the internal energy change Δu of hydrogen in kJkg as it is heated from 200 to 800 K using a the empirical specific heat equation as a function of temperature Table A2c b the cv value at the average temperature Table A2b.
The system had 30 cal exothermic reaction and 05 cal compression. Calculate change in internal energy when Question Calculate change in internal energy when 5 mole of hydrogen is heated to 2 0 0 C from 1 0 0 C specific heat of hydrogen at constant pressure is 8cal m o l 0 C 1. Now we will use the empirical relation for part A which says for which is for CP as a function of T and we get this from our table and were.
The system absorbed 20 cal heat and the volume became twice with 010 cal work d. The internal energy change textbf internal energy change internal energy change Δ u Delta u Δ u is then calculated by dividing the internal energy per mole with the molar mass of the hydrogen M 2016 kg kmol 1 M2016text kgtext kmol-1 M 2016 kg kmol 1.
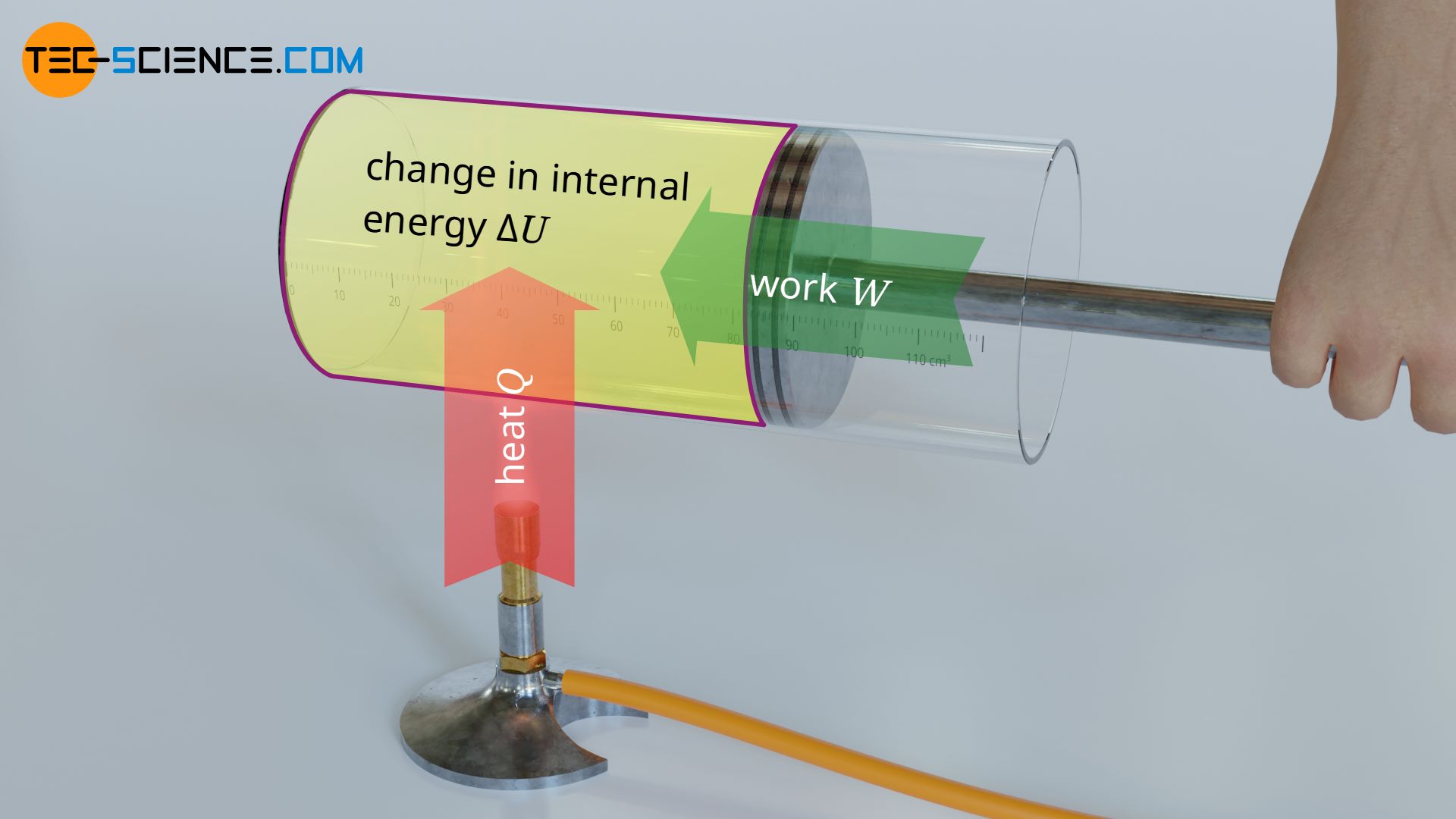
Calculation Of The Internal Energy For Ideal Gases Tec Science
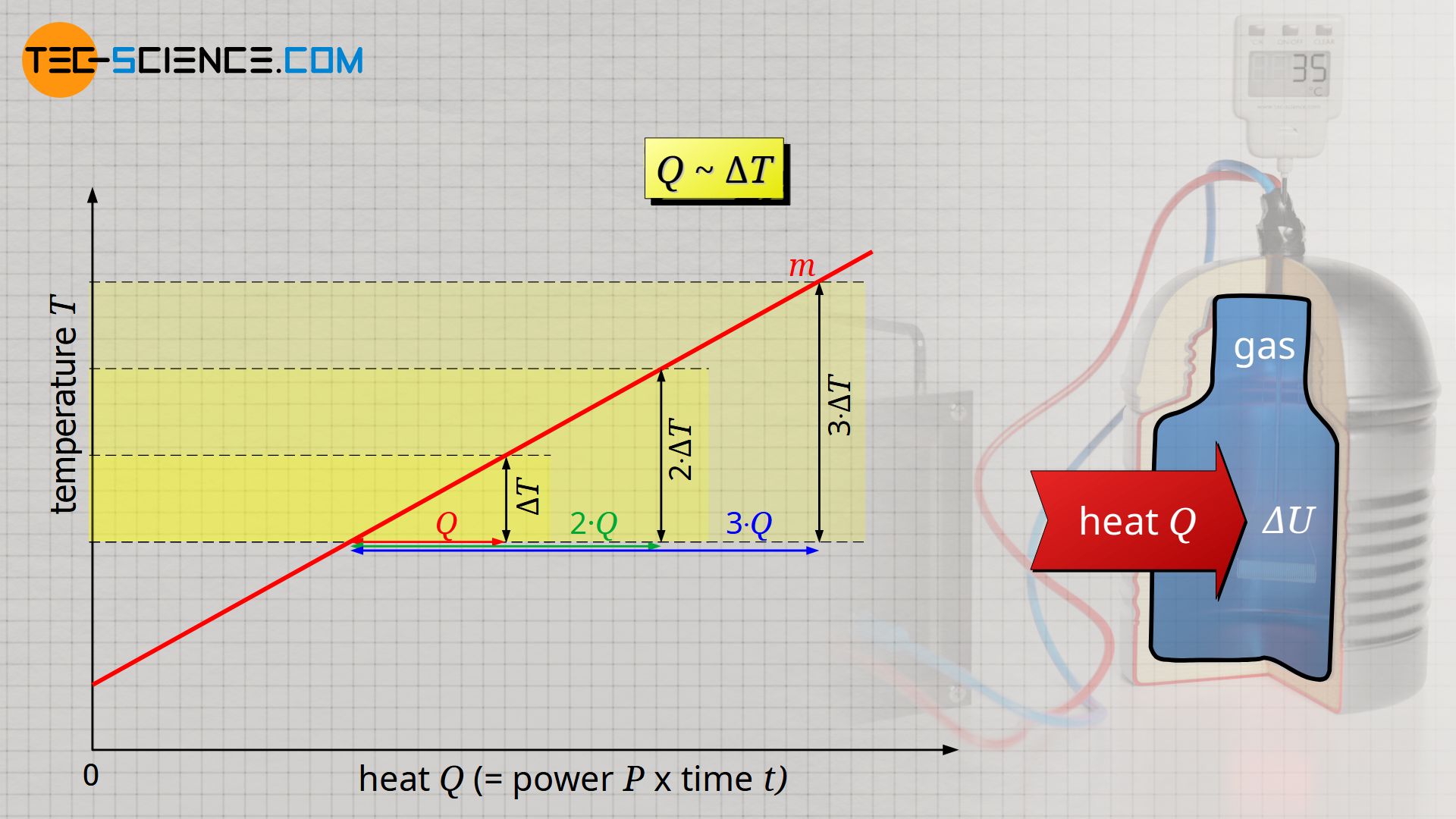
Calculation Of The Internal Energy For Ideal Gases Tec Science

Chapter 3a The First Law Closed Systems Energy Updated 1 17 11
Comments
Post a Comment